XOR-SAT — различия между версиями
(→Решение XOR-SAT задачи методом Гаусса) |
(→Решение XOR-SAT задачи методом Гаусса) |
||
| Строка 252: | Строка 252: | ||
!class="dark"| <tex>c</tex> | !class="dark"| <tex>c</tex> | ||
!class="dark"| <tex>d</tex> | !class="dark"| <tex>d</tex> | ||
| − | !class="green"| | + | !class="green" style="font-weight:normal" style="background: #ddffdd;"| |
|Операция | |Операция | ||
|-align="center" | |-align="center" | ||
| Строка 275: | Строка 275: | ||
!class="green" style="font-weight:normal" style="background: #ddffdd;"| <tex>0</tex> | !class="green" style="font-weight:normal" style="background: #ddffdd;"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| <tex>J=G \oplus H</tex> | | <tex>J=G \oplus H</tex> | ||
| + | |-align="center" | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>1</tex> | ||
| + | !class="green" style="font-weight:normal" style="background: #ddffdd;"| <tex>1</tex> | ||
| + | | <tex>H</tex> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" align="center" style="color: blue; background-color:#ffffcc;" cellpadding="10" | ||
| + | |+ | ||
| + | |-align="center" | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>1</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="green" style="font-weight:normal" style="background: #ddffdd;"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | | <tex>K=I \oplus J</tex> | ||
| + | |-align="center" | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>1</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="green" style="font-weight:normal" style="background: #ddffdd;"| <tex>1</tex> | ||
| + | | <tex>L=E \oplus J</tex> | ||
| + | |-align="center" | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>1</tex> | ||
| + | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | !class="green" style="font-weight:normal" style="background: #ddffdd;"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| + | | <tex>J</tex> | ||
|-align="center" | |-align="center" | ||
!class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | !class="dark" style="font-weight:normal"| <tex>0</tex> | ||
| Строка 284: | Строка 315: | ||
|} | |} | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Следствие:<tex>R</tex>(<tex>a</tex>,<tex>c</tex>,<tex>d</tex>)<tex>\land</tex> <tex>R</tex>(<tex>b</tex>,<tex>\neg c</tex>,<tex>d</tex>)<tex>\land</tex><tex>R</tex>(<tex>a</tex>,<tex>b</tex>,<tex>\neg d</tex>)<tex>\land</tex><tex>R</tex>(<tex>a</tex>,<tex>\neg b</tex>,<tex>\neg c</tex>)<font color='red'>∧ R(¬a,b,c)</font> | ||
==Вычислительная сложность== | ==Вычислительная сложность== | ||
Версия 14:01, 5 января 2017
| Задача: |
| (XOR-satisfiability) выполнимость функции — задача распределения аргументов в булевой КНФ функции, записанной в виде XOR-КНФ, таким образом, чтобы результат данной функции был равен . |
Содержание
Описание
Одним из особых случаев является класс задач, где каждый конъюнкт содержит операции (т. е. исключающее или), а не (обычные) операторы.(Формально, обобщенная КНФ с тернарным булевым оператором R работает только если или переменные дают в своих аргументах. Конъюнкты,имеющие более переменных могут быть преобразованы в сочетании с формулой преобразования с сохранением выполнимости булевой функции, т. е. - может быть снижена до --)[1]
Это задача Р-класса,так как - формулу можно рассматривать как систему линейных уравнений по модулю ,которая ,в свою очередь, может быть решена за методом Гаусса [2].Такое представление возможно на основе связи между Булевой алгеброй и Булевым кольцом [3] и том факте,что арифметика по модулю образует конечное поле [4].
Решение XOR-SAT задачи методом Гаусса
| Система уравнений | |
|---|---|
| ("" означает «», "" означает «»)
Каждый конъюнкт ведет к одному уравнению. |
|
| Переменные | Значение |
| Нормированная система уравнений | |
|---|---|
| Используя свойства Булевых колец
(, ) |
|
| Переменные | Значение |
| Матрица соответствующих коэффициентов | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Строка | |||||
| Преобразования, чтобы сформировать
верхнюю треугольную матрицу | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Операция | |||||
| Преобразования, чтобы сформировать
диагональную матрицу | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Операция | |||||
Следствие:(,,) (,,)(,,)(,,)∧ R(¬a,b,c)
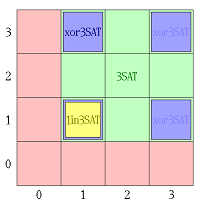
Вычислительная сложность
Поскольку принимает значение ,если и только если из переменных {,,} принимает значение ,каждое решение в --- задачи для данной КНФ-формулы является также решением -- задачи, и ,в свою очередь,обратное также верно.
Как следствие, для каждой КНФ-формулы, можно решить ---задачу и на основании результатов сделать вывод, что либо - задача решаема или, что ----задача нерешаема.
При условии ,что P- и NP-классы не равны,ни -,ни Хорн-,ни - не являются задачи NP-класса,в отличии от .
См. также
Примечания
- ↑ Alfred V. Aho; John E. Hopcroft; Jeffrey D. Ullman.The Design and Analysis of Computer Algorithms. Addison-Wesley.; здесь: Thm.10.4, 1974.
- ↑ Метод Гаусса
- ↑ Связь между Булевой алгеброй и Булевым кольцом
- ↑ Конечное поле
Источники информации
- Википедия — Boolean satisfiability problem
- Cook, Stephen A.Proceedings of the 3rd Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing: 151–158, 1971.